Utilizing Bio-Based
Polymer Materials to Remove Dye from Aqueous Solutions
Water supplies continue to be insufficient due to global climate change, fast population increase, and industrialization, and our current resources are degraded by careless usage, posing a severe issue.
Despite the fact that water supplies are fast running out, wastewater treatment alone is insufficient. Reusing cleaned wastewater in a sustainable manner is equally crucial. Both the economy and a sustainable environment benefit from the treatment and reuse of waste water.
Domestic and industrial operations produce waste water that contains potentially hazardous
contaminants. The untreated discharge of printing and dyeing industry industrial wastes into lakes, rivers, and streams contributes significantly to the development of water pollution.
It is estimated that more than 10,000 different dyes and pigments are used industrially worldwide and approximately 0.7 million tons of dyes are synthesized each year. Considering the pollution caused by dye wastes produced in very high quantities, studies on
wastewater treatment are important.
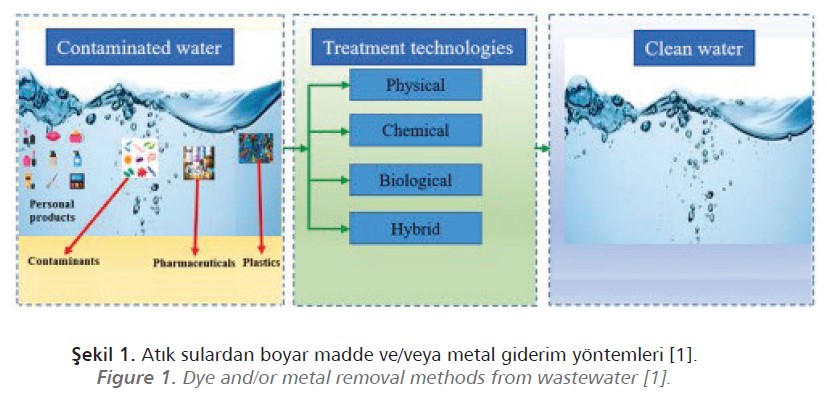
According to a survey by Fortune Business Insights, the size Metal and/or dye removal from wastewater is performed using physical, chemical, and biological techniques. Sieves, screens, grit traps, floating matter traps, balancing and settling pools are examples
of physical treatment techniques.
Using a variety of chemicals, pollutants that cannot be physically treated and precipitated are eliminated from the environment. Chemical-based removal techniques include
coagulation, flocculation, disinfection, and ion exchange.
The adsorption technique is recommended as the best method for eliminating a variety of contaminants since it is effective, simple to use, and economical to operate on an industrial scale.
The choice of adsorbent is crucial because it affects the cost, capacity, and selectivity of the process as well as the removal of wastewater via adsorption.
It is possible to categorize adsorbents as natural (clay, zeolite, fly ash), artificial (silica gels, resins, polymers), or bio-adsorbents, according to the adsorbent source (chitin, chitosan, yeast, fungal and bacterial biomass, etc.). Due to their effective adsorption capability and relatively simple fabrication procedure, polymeric adsorbents are often used.
Recent years have seen a rise in the number of literature research on bio-based polymers made from cheap, safe, and biodegradable natural raw sources. In the production of bio-based polymers, chitin, chitosan, cellulose, aliginate, lignin, starch-based substances are
used as raw materials, as well as polyethylene glycol (PEG) structured molecules for biodegradability.
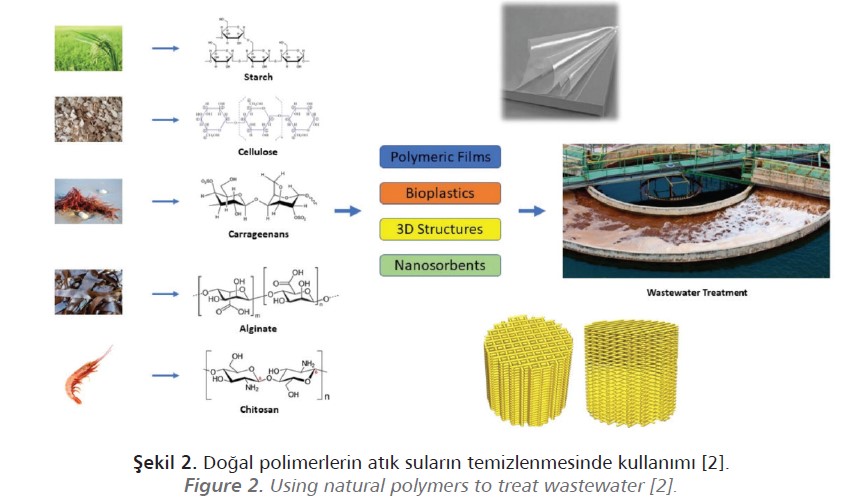
At the Izel Kimya R&D Center, several projects are being carried out to remove paint and metal from waste water in an effort to support the fight against environmental pollution.
References:
1. S.F. Ahmed, M. Mofijur, Samiha Nuzhat, Anika Tasnim Chowdhury, Nazifa Rafa, Md. Alhaz Uddin, Abrar Inayat, T.M.I. Mahlia,
Hwai Chyuan Ong, Wen Yi Chia, Pau Loke Show, Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques
for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 416, 2021, 125912, ISSN 0304-
3894, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125912.
2. Russo, T.; Fucile, P.; Giacometti, R.; Sannino, F. Sustainable Removal of Contaminants by Biopolymers: A Novel Approach for Wastewater
Treatment. Current State and Future Perspectives. Processes 2021, 9, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040719
3. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/water-and-wastewater-treatment-market-102632
4. N. Khan,ST Hussain, A. Saboor, N. Jamila, KS Kim, Int. J. Phys. Bilim ,8(33), 1661 (2013).
5. A. B. dos Santos, F. J. Cervantes, and J. B. van Lier, (2007), “Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile
wastewaters: perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 98, no. 12, pp. 2369–2385.
6. Ranade, V. V., Bhandari, V. M., (2014), “Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse: An Overview”, Elsevier, Oxford,
Chapter 1.
7. Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E. (2018), “Wastewater Treatment: An Overview.”, Green Adsorbents For Pollutant Removal, pp.1-21.)
Dr. Cemil Dizman R&D Manager
İzel Kimya
Aleyna Turanlı
R&D Researcher
İzel Kimya
 According to a survey by Fortune Business Insights, the size Metal and/or dye removal from wastewater is performed using physical, chemical, and biological techniques. Sieves, screens, grit traps, floating matter traps, balancing and settling pools are examples
of physical treatment techniques.
Using a variety of chemicals, pollutants that cannot be physically treated and precipitated are eliminated from the environment. Chemical-based removal techniques include
coagulation, flocculation, disinfection, and ion exchange.
The adsorption technique is recommended as the best method for eliminating a variety of contaminants since it is effective, simple to use, and economical to operate on an industrial scale.
The choice of adsorbent is crucial because it affects the cost, capacity, and selectivity of the process as well as the removal of wastewater via adsorption.
It is possible to categorize adsorbents as natural (clay, zeolite, fly ash), artificial (silica gels, resins, polymers), or bio-adsorbents, according to the adsorbent source (chitin, chitosan, yeast, fungal and bacterial biomass, etc.). Due to their effective adsorption capability and relatively simple fabrication procedure, polymeric adsorbents are often used.
Recent years have seen a rise in the number of literature research on bio-based polymers made from cheap, safe, and biodegradable natural raw sources. In the production of bio-based polymers, chitin, chitosan, cellulose, aliginate, lignin, starch-based substances are
used as raw materials, as well as polyethylene glycol (PEG) structured molecules for biodegradability.
According to a survey by Fortune Business Insights, the size Metal and/or dye removal from wastewater is performed using physical, chemical, and biological techniques. Sieves, screens, grit traps, floating matter traps, balancing and settling pools are examples
of physical treatment techniques.
Using a variety of chemicals, pollutants that cannot be physically treated and precipitated are eliminated from the environment. Chemical-based removal techniques include
coagulation, flocculation, disinfection, and ion exchange.
The adsorption technique is recommended as the best method for eliminating a variety of contaminants since it is effective, simple to use, and economical to operate on an industrial scale.
The choice of adsorbent is crucial because it affects the cost, capacity, and selectivity of the process as well as the removal of wastewater via adsorption.
It is possible to categorize adsorbents as natural (clay, zeolite, fly ash), artificial (silica gels, resins, polymers), or bio-adsorbents, according to the adsorbent source (chitin, chitosan, yeast, fungal and bacterial biomass, etc.). Due to their effective adsorption capability and relatively simple fabrication procedure, polymeric adsorbents are often used.
Recent years have seen a rise in the number of literature research on bio-based polymers made from cheap, safe, and biodegradable natural raw sources. In the production of bio-based polymers, chitin, chitosan, cellulose, aliginate, lignin, starch-based substances are
used as raw materials, as well as polyethylene glycol (PEG) structured molecules for biodegradability.
 At the Izel Kimya R&D Center, several projects are being carried out to remove paint and metal from waste water in an effort to support the fight against environmental pollution.
References:
1. S.F. Ahmed, M. Mofijur, Samiha Nuzhat, Anika Tasnim Chowdhury, Nazifa Rafa, Md. Alhaz Uddin, Abrar Inayat, T.M.I. Mahlia,
Hwai Chyuan Ong, Wen Yi Chia, Pau Loke Show, Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques
for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 416, 2021, 125912, ISSN 0304-
3894, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125912.
2. Russo, T.; Fucile, P.; Giacometti, R.; Sannino, F. Sustainable Removal of Contaminants by Biopolymers: A Novel Approach for Wastewater
Treatment. Current State and Future Perspectives. Processes 2021, 9, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040719
3. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/water-and-wastewater-treatment-market-102632
4. N. Khan,ST Hussain, A. Saboor, N. Jamila, KS Kim, Int. J. Phys. Bilim ,8(33), 1661 (2013).
5. A. B. dos Santos, F. J. Cervantes, and J. B. van Lier, (2007), “Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile
wastewaters: perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 98, no. 12, pp. 2369–2385.
6. Ranade, V. V., Bhandari, V. M., (2014), “Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse: An Overview”, Elsevier, Oxford,
Chapter 1.
7. Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E. (2018), “Wastewater Treatment: An Overview.”, Green Adsorbents For Pollutant Removal, pp.1-21.)
Dr. Cemil Dizman R&D Manager
İzel Kimya
Aleyna Turanlı
R&D Researcher
İzel Kimya
At the Izel Kimya R&D Center, several projects are being carried out to remove paint and metal from waste water in an effort to support the fight against environmental pollution.
References:
1. S.F. Ahmed, M. Mofijur, Samiha Nuzhat, Anika Tasnim Chowdhury, Nazifa Rafa, Md. Alhaz Uddin, Abrar Inayat, T.M.I. Mahlia,
Hwai Chyuan Ong, Wen Yi Chia, Pau Loke Show, Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques
for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 416, 2021, 125912, ISSN 0304-
3894, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125912.
2. Russo, T.; Fucile, P.; Giacometti, R.; Sannino, F. Sustainable Removal of Contaminants by Biopolymers: A Novel Approach for Wastewater
Treatment. Current State and Future Perspectives. Processes 2021, 9, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040719
3. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/water-and-wastewater-treatment-market-102632
4. N. Khan,ST Hussain, A. Saboor, N. Jamila, KS Kim, Int. J. Phys. Bilim ,8(33), 1661 (2013).
5. A. B. dos Santos, F. J. Cervantes, and J. B. van Lier, (2007), “Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile
wastewaters: perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 98, no. 12, pp. 2369–2385.
6. Ranade, V. V., Bhandari, V. M., (2014), “Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse: An Overview”, Elsevier, Oxford,
Chapter 1.
7. Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E. (2018), “Wastewater Treatment: An Overview.”, Green Adsorbents For Pollutant Removal, pp.1-21.)
Dr. Cemil Dizman R&D Manager
İzel Kimya
Aleyna Turanlı
R&D Researcher
İzel Kimya