Colostrum: Elixir of Life
The decision to transition into motherhood or continue raising your family is a pretty serious one, and you’ve probably developed some concerns about how you can take care of and feed your baby... Believe it or not, the female body has miraculously provided clues about this important experience before them. Since ancient times “Do not worry!” There is a power that says. So far, you’ve researched the miraculous benefits of breast milk, heralded as the perfect diet for your little one. But there is more. Colostrum.
The breasts first secrete colostrum (which it has been producing since mid-pregnancy) (which it has actually been producing since mid-pregnancy), a rich, sticky, clear or yellow substance that has earned it the title “Liquid Gold.” This protein-packed liquid is truly invaluable when it comes to feeding your baby.
Colostrum is often overlooked, but remains a vital substance for the baby. While mothers can produce colostrum during their pregnancy, it is not until after the birth of the placenta that hormonal shifts in their bodies encourage the release of colostrum which allows the baby to start breastfeeding and feeding soon after birth. As baby’s first meal, colostrum provides the nutrients and nourishment the baby needs. Better still, this powerful vitamin-packed liquid is uniquely tailored to the baby.
If we look at it from a scientific and medical approach, the breasts of pregnant women change in size and appearance with the effect of estrogen and progesterone hormones.
The alveolar cells of the breast begin to secrete colostrum during the twelfth to sixteenth week of pregnancy. This is called lactogenesis I. Colostrum is a thick, yellowish-white
liquid that can be secreted from the breast during the third trimester. During pregnancy, milk secretion is suppressed by estrogen and progesterone.(1)
Colostrum contains more protein and less carbohydrates and fats than mature breast milk. Colostrum is rich in secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA), which helps protect the baby from infection. Colostrum also helps establish a normal gut microbiome in the baby. The intestine is considered sterile at birth.
Colostrum, called the first milk, is secreted immediately after birth. It is usually slightly darker in color than breast milk. The color tone such as light brown, dark yellow can
be in different tones from person to person. However, its distinguishing feature in this regard is that it is dark colored, not white like breast milk. The consistency of colostrum is again slightly denser than breast milk. Like cream, it can be expected to have a less runny consistency than milk.
Human colostrum is the ideal food for newborn humans and is preferred over formula or milk from other animals. The proportions of nutrients in human milk are different from those of other animals and therefore more suitable for humans. Although the formula mimics human milk as much as possible, the components of colostrum and mature milk such as immunoglobulins, leukocytes, as well as antioxidants, enzymes and hormones give colostrum and mature breast milk many advantages over formula. This is vitally important for preterm babies, who are much more vulnerable to infection and benefit greatly from taking colostrum and breast milk.
Powder Colostrum as a Life Science Ingredients is derived from cow colostrum.
Just as we mentioned above the vital effects of colostrum on Human as a mammal and its offspring, its effect on another mammal, the Cow, and its calf, determines whether they will live for the first 2 hours and what kind of cow they will be for the first 2 months.
Colostrum is the secretion in the mammary glands of cows in the first 24 hours after birth. Colostrum is different from normal milk in terms of content, physical properties and functionality. Colostrum transitional milk is the milk secreted between the 24th and 72nd hours after birth. The milk secreted for 72 hours after birth shows changes. Colostrum contains much more dry matter, protein and immunoglobulin (Ig) than normal milk. It is very important that the calf receives these immune substances from its mother within the first 24 hours after it is born.
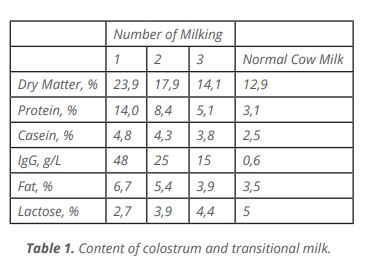
Immunoglobulins (antibodies) are immune substances that detect and destroy pathogens in the animal. There are three types of immunoglobulins in bovine colostrum; IgG,
IgM and IgA. New born calves have not developed defense mechanisms against diseases, but these immunoglobulins, which they receive with the first milk secreted from the
mother, provide passive protection to the calf until the calf forms its own active immune system. Colostrum contains 70-80% IgG, 10-15% IgM and 10-15% IgA.
Recognized classes of immunoglobulins in mammals:
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
Immunoglobulin D (IgD)
The most common class of immunoglobulin in all species is IgG. IgGs pass from cow’s blood to colostrum by a special transport route. This mechanism allows a large number of IgGs to pass from the blood to the breast. As a result, the serum IgG ratio of the mother starts to decrease 2-3 weeks before the birth. The cow can replace this lost IgG a few weeks after birth. IgM and IgA are synthesized from plasmocytes in the mammary glands.
Functions of Immunoglobulins
Each Immunoglobulin has a different task. The most bundant immunoglobulin in colostrum and serum is IgG. The primary task of IgG is to detect and destroy invading pathogens. Because the size of IgG is smaller than other immunoglobulins, so it can go to other parts of the body. IgM acts as the first line of defense in case of septicemia. Since IgM is a large molecule, it stays in the blood and provides protection against invading bacteria. IgA protects mucosal surfaces such as the gut. By adhering to the intestinal surface, it prevents the attachment of pathogens and causing disease. By feeding colostrum for 3 days, you encourage the adhesion and protection of IgA to the intestinal surface.
Colostrum contains high amounts of IgG and lesser amounts of IgM and IgA. These three immunoglobulins play a very important role in reducing the calf’s chance of getting sick or dying. However, it should not be forgotten that colostrum feeding and the immunoglobulins in it are only one of the things needed to protect the calf. Proper feeding and housing conditions are other factors that help the calf to be healthy.
Let’s talk about the contributions of Colostrum, which effectively protects the immune system of infant, child, adult and geriatric humanity, to our health:
Immunization: With powerful immune-boosting properties, colostrum contains antibodies and provides protection against environmental germs and internal inflammation. (it helps to destroy those harmful microorganisms!) It contributes significantly to the healthy, long-term development of your baby.
Gut Health: Colostrum is easy to digest and helps line the gut with a protective layer that safeguards against future infections and diseases. It also encourages the growth of good bacteria.
• It can restore a leaky gut lining to normal permeability levels and reduce the movement of toxins and gut microbes into the bloodstream.
Nutrition Rich in Nutrition: It is a “Super Food” class food.

Body Regulation: Colostrum regulates body temperature, blood sugar, metabolism, lung and vascular functions
• Supports muscle and ligament healing.
• High levels of growth factors and antioxidants are a powerhouse to support muscle recovery and growth.
• Our bodies are constantly regenerated – muscle, skin, bone, brain and nerve tissue regeneration has been proven.
• A great supplement for athletes (some athletes have used colostrum to improve their performance) shorten recovery time and prevent illness at peak performance levels.
• Helps desensitize the body to allergens - preventative, inhibiting allergic reactions by helping to suppress IgE expression.
• Multiple immune factors and natural antibiotics provide strong support to the immune system.
• Activate the production of anti-disease antibodies
• Colostrum has been shown to be almost as effective as the flu vaccine. (2)
Our Powder Colostrum producer collects cow colostrum (liquid raw material) only from Czech farms under the strict control of the Czech Veterinary Administration. Then,
it provides the preservation of bioactive substances such as IgG by processing with microfiltration, not by heat treatment such as pasteurization or sterilization.
Microfiltration is a very modern, gentle and alternative to heat treatment. Thanks to the cold microfiltration process, active substances (immunoglobulins, growth factors, etc.)
are kept active. A gentle spray dryer is used to dry it into powder form, resulting in colostrum standardized for IgG content.
References
(1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513256/
(2) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17456621
Burak Kamal
Business Development Manager
Barentz

 Immunoglobulins (antibodies) are immune substances that detect and destroy pathogens in the animal. There are three types of immunoglobulins in bovine colostrum; IgG,
IgM and IgA. New born calves have not developed defense mechanisms against diseases, but these immunoglobulins, which they receive with the first milk secreted from the
mother, provide passive protection to the calf until the calf forms its own active immune system. Colostrum contains 70-80% IgG, 10-15% IgM and 10-15% IgA.
Immunoglobulins (antibodies) are immune substances that detect and destroy pathogens in the animal. There are three types of immunoglobulins in bovine colostrum; IgG,
IgM and IgA. New born calves have not developed defense mechanisms against diseases, but these immunoglobulins, which they receive with the first milk secreted from the
mother, provide passive protection to the calf until the calf forms its own active immune system. Colostrum contains 70-80% IgG, 10-15% IgM and 10-15% IgA.
 Body Regulation: Colostrum regulates body temperature, blood sugar, metabolism, lung and vascular functions
• Supports muscle and ligament healing.
• High levels of growth factors and antioxidants are a powerhouse to support muscle recovery and growth.
• Our bodies are constantly regenerated – muscle, skin, bone, brain and nerve tissue regeneration has been proven.
• A great supplement for athletes (some athletes have used colostrum to improve their performance) shorten recovery time and prevent illness at peak performance levels.
• Helps desensitize the body to allergens - preventative, inhibiting allergic reactions by helping to suppress IgE expression.
• Multiple immune factors and natural antibiotics provide strong support to the immune system.
• Activate the production of anti-disease antibodies
• Colostrum has been shown to be almost as effective as the flu vaccine. (2)
Our Powder Colostrum producer collects cow colostrum (liquid raw material) only from Czech farms under the strict control of the Czech Veterinary Administration. Then,
it provides the preservation of bioactive substances such as IgG by processing with microfiltration, not by heat treatment such as pasteurization or sterilization.
Microfiltration is a very modern, gentle and alternative to heat treatment. Thanks to the cold microfiltration process, active substances (immunoglobulins, growth factors, etc.)
are kept active. A gentle spray dryer is used to dry it into powder form, resulting in colostrum standardized for IgG content.
Body Regulation: Colostrum regulates body temperature, blood sugar, metabolism, lung and vascular functions
• Supports muscle and ligament healing.
• High levels of growth factors and antioxidants are a powerhouse to support muscle recovery and growth.
• Our bodies are constantly regenerated – muscle, skin, bone, brain and nerve tissue regeneration has been proven.
• A great supplement for athletes (some athletes have used colostrum to improve their performance) shorten recovery time and prevent illness at peak performance levels.
• Helps desensitize the body to allergens - preventative, inhibiting allergic reactions by helping to suppress IgE expression.
• Multiple immune factors and natural antibiotics provide strong support to the immune system.
• Activate the production of anti-disease antibodies
• Colostrum has been shown to be almost as effective as the flu vaccine. (2)
Our Powder Colostrum producer collects cow colostrum (liquid raw material) only from Czech farms under the strict control of the Czech Veterinary Administration. Then,
it provides the preservation of bioactive substances such as IgG by processing with microfiltration, not by heat treatment such as pasteurization or sterilization.
Microfiltration is a very modern, gentle and alternative to heat treatment. Thanks to the cold microfiltration process, active substances (immunoglobulins, growth factors, etc.)
are kept active. A gentle spray dryer is used to dry it into powder form, resulting in colostrum standardized for IgG content.
